Let’s say x is uniformly distributed with beginning a = 20 and ending b = 40, Now solve the below questions.
- Calculate P(x>30)
- Calculate P(30<x<80)
- Calculate P(0<x<10)
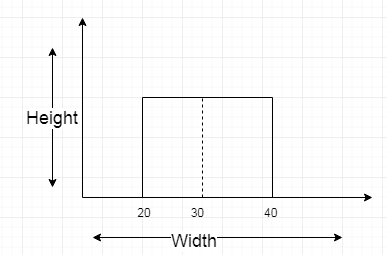
We already seen how to calculate height and width(Qbase) in our previous post.If the draw a uniform distribution for the given parameters this how it looks like
Calculate P(x>30)
We need to find the probability of x is greater than 30 from the below normal distribution.
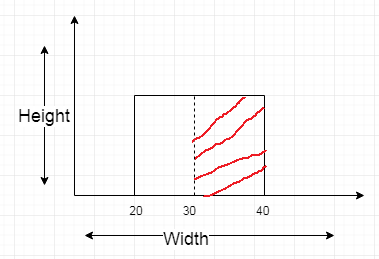
P(x>30) = width * height
Calculate Height:
Width = 40 -20 =20
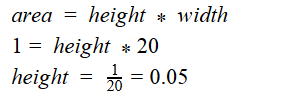
Calculate Width:
in our case we need to find the width between 40 and 30 as we need to find P(x>30)
So P(x>30) = 10*0.05= 0.5
So chances of P(x>30) is with 50% probability.
Calculate P(30<x<80)
In our case a= 20 and b= 40, means we don’t have 80 and we already calculate P(x>30)..
As we know P(x>30) will be equal to P(30<x) or P(x<30), because 30 will be in between 20 and 40 there will be equal chances of P(x>30) and P(x<30)
So P(30<x<80) will be 50% chances.
Calculate P(0<x<10):
Simple the probability of P(0<x<10) will be zero as we have parameters between 20 and 40.