Prerequisites:
Install NLTK using pip install nltk
We will see the below basic Natural Language processing topic in this article
- Tokenization
- Stop words
- Stemming
- Lemmatization
Tokenization:
Tokenization is the process in which a sequence of words is broken into pieces as words. Again we have two parts of Tokenization
- Word tokenization
- Sentence Tokenization
Word tokenization:
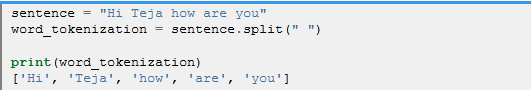
A Sequence of words(paragraph) is broken in to individual words(list of words),Lets take a sentence “Hi Teja how are you” if we tokenize it the results will be like [“Hi”,”Teja”,”how”,”are”,”you”]
In python we have a famous option for word tokenization using string method called split().
Sentence Tokenization:
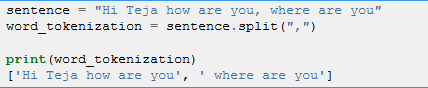
The only difference with word tokenization is in word tokenization we split the paragraph with space and in sentence tokenization we will split based on “.” or “,”. We use split(“,”) or split(“.”) or split(“\n”)
Stop words:
This is also one of major common step that need to be performed at initial stage during Natural language processing, this steps will removes most common words like “the,and,is,for” etc.. because this words wont make any sense in Natural Language processing.
In the below python code we are using sent_tokenize() methods which is present in NLTK library, we are using sentence tokenize as we have more than one sentence in our case as shown in the below code, we can also directly use word tokenize after removing the punctuation.
data = """I am data science engineer. who will take care of Machine learning and data engineer. currently based out of bangalore""" sentence_tokenize = nlp.sent_tokenize(data) #Printing the response of sentence tokenze print(sentence_tokenize) ['I am data science engineer.', 'who will take care of Machine learning and data engineer.', 'currently based out of bangalore']
Below is the python code for stop words
from nltk.corpus import stopwords # we are using for loop to loop into each sentence for i in range(len(stop_words)): # Now each sentence we are tokenizing to words words = nlp.word_tokenize(stop_words[i]) #Now removing the stop words using list comprehensive looping the word tokenize and cheking if stop words are present words = [word for word in words if word not in stopwords.words('english')] # using join methods we are converting list of words into string stop_words[i] = ' '.join(words)
Below is the response after we apply stop words.if you observe we removed words like “am,who,will” etc..
print(stop_words) ['I data science engineer .', 'take care Machine learning data engineer .', 'currently based bangalore']
Stemming : Stemming is the process of a change in the form of a word (typically at the ending its main concern is removing the common endings to words ) to their root forms such as mapping a group of words to the same stem. The stem itself is not a valid word in the Language,Below is the best example to understand stemming, if you see studi has no meaning
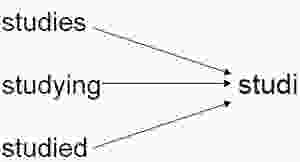
Stemming has three different types as shown below
- Port stemmer : It is the first version of stemming released in 1980
- Snowball stemmer : Latest version of port stemmer
- Lancaster stemmer : We can customize our own rules for stemming
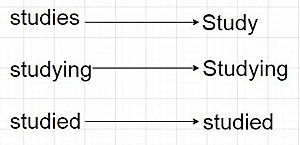
In our example we used port stemmer Lemmatization: It is same as stemming but the result will be some what meaning full,it is the root form representation of a given word. It will convert all words having the same meaning but different representation to their base form as shown below
Stemming vs Lemmatization:
| Stemming | Leematization |
| The outcome word has no meaning | The outcome word has meaning |
| It takes less time as it just removed the common end words | It takes long time as it must search for the root meaningful word |
| We can use when the meaning of the word is not important like Spam detection | We can use when the meaning of the word is important like sentiment analysis, chat bots |
you can download the full source code from https://github.com/tejadata/spark/blob/master/NLP_stemming_Lemmatization.py