- A binomial distribution is a probability of SUCCESS or FAILURE in an experiment that is repeated many times.
- It is call Binominal because we will have only two outcomes.
- Binomial is a discrete because the values are fixed
For Eg: I want to roll a dice and expecting six, I will either get six (SUCCESS) or any other values(FAILURE),here I might get the value from 1 to 6 , but not 1.1,1.23 etc..
In short anything you think about SUCCESS or FAILURE like if I propose my love to my dream girl, Will she accepts or not(SUCCESS or FAILURE )
We will understand more with below examples between SUCCESS and FAILURE.
What is the probability of getting heads when I toss a coin.
If we are expecting a heads then heads will be SUCCESS and tails will be FAILURE.Below is the probability of SUCCESS and FAILURE.

We have two formulas to calculate the Binomial Distribution.
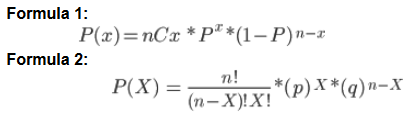
Where:
b = binomial probability
x = total number of “successes” (pass or fail, heads or tails etc.)
P = probability of a success on an individual trial
Q = probability of a failure (means 1-P)
n = number of trials
We need to understand how to calculate combinations and factorial,click here to know
We will take one example and solve the Binomial problem.
A coin is tossed 10 times. What is the probability of getting exactly 4 heads?
From our question
n=10
x=4
p=0.5
q=1-p=0.5
We will use Formula 2 to calculate
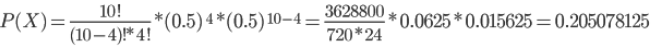
So there will be 20.5% probability of getting 4 heads when I toss 10 times.